What is the best painkiller for spinal stenosis? Spinal stenosis is a medical condition characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can put pressure on the nerves and cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the legs and back. Effective management of spinal stenosis pain requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates various treatment options.
In this discussion, we will explore the different types of painkillers used to treat spinal stenosis pain, including over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications, as well as alternative therapies and lifestyle changes.
Understanding Spinal Stenosis
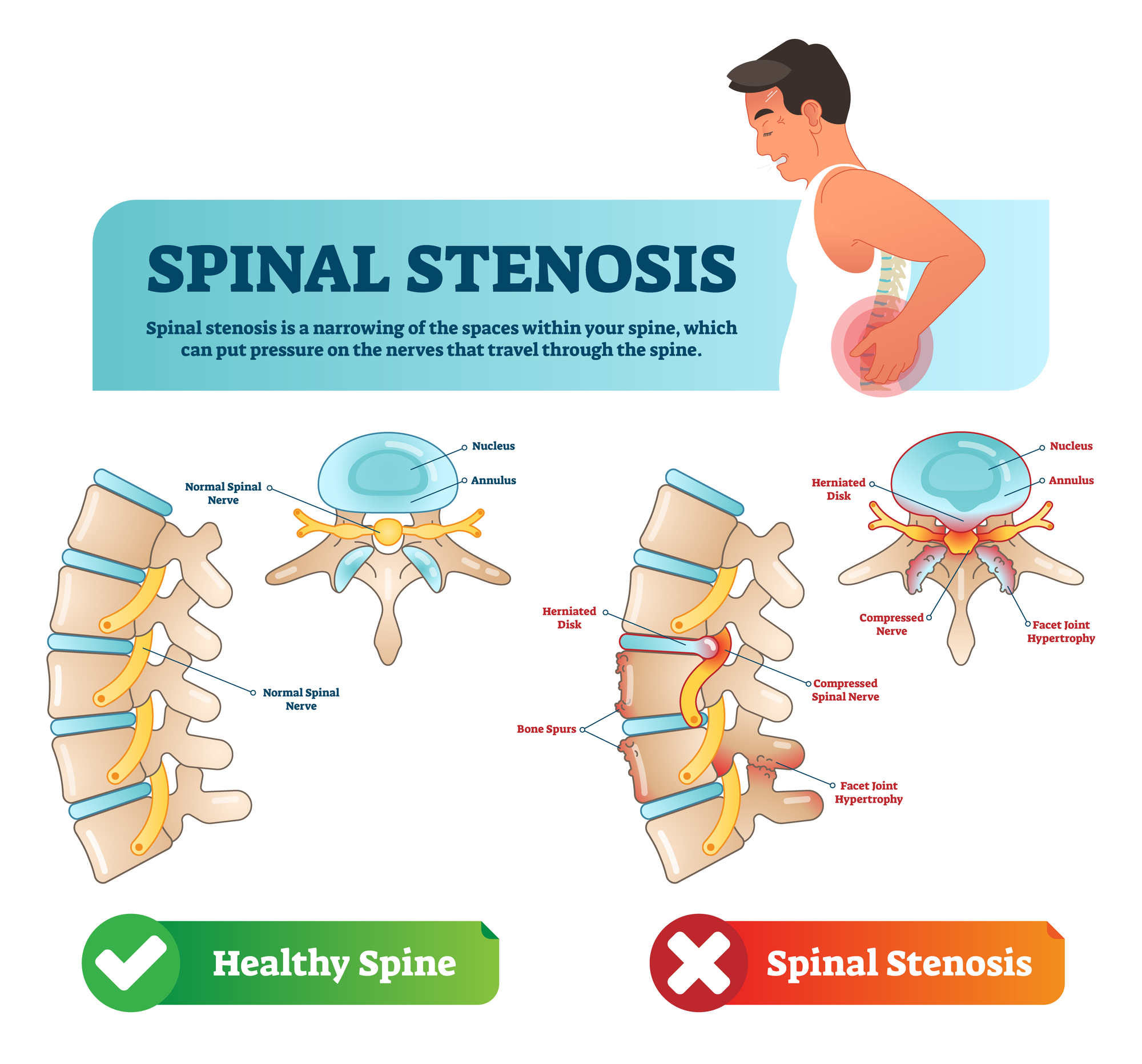
Spinal stenosis is a medical condition characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This condition can cause pain, numbness, weakness, and tingling sensations in various parts of the body. Spinal stenosis can be caused by a combination of factors, including degenerative disc disease, spinal injuries, spinal tumors, and spinal fractures.
The Causes of Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis can occur due to various factors, including:
- Degenerative disc disease: Wear and tear on the spinal discs can cause them to shrink, leading to a narrowing of the spinal canal.
- Spinal injuries: Traumatic injuries to the spine can cause compression or herniation of the spinal discs, leading to spinal stenosis.
- Spinal tumors: Tumors can grow in the spine, compressing the spinal cord and nerves.
- Spinal fractures: Fractures of the spine can cause instability and narrowing of the spinal canal.
- Genetic conditions: Certain genetic conditions, such as achondroplasia, can cause spinal stenosis.
The specific cause of spinal stenosis can often be determined through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans.
Common Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis
The symptoms of spinal stenosis can vary depending on the location and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Pain in the back, legs, or arms.
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the back, legs, or arms.
- Weakness in the legs or arms.
- Difficulty walking or standing for long periods.
- Difficulty with balance and coordination.
- Difficulty with bladder or bowel function.
These symptoms can worsen with activities that involve bending, twisting, or lifting, and can improve with rest.
The Role of Nerve Compression in Spinal Stenosis Pain
The pain associated with spinal stenosis is often caused by compression of the spinal nerves. When the spinal canal becomes narrowed, the nerves that pass through it can become compressed, leading to pain, numbness, and tingling sensations. The compression of the nerves can also lead to inflammation and scarring, which can further exacerbate the symptoms of spinal stenosis. The degree of pain and discomfort associated with spinal stenosis can vary widely from person to person and can range from mild to severe.
Pain Management Options
Pain management is a crucial aspect of living with spinal stenosis. Effective pain management can help improve the quality of life for individuals with spinal stenosis by reducing pain, promoting mobility, and enabling them to perform daily activities with greater ease.
Types of Painkillers
Spinal stenosis pain can be effectively managed with a range of painkillers. These painkillers can be broadly categorized into over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications. OTC painkillers are available without a doctor’s prescription and are generally considered safer for long-term use. Prescription painkillers, on the other hand, are available only with a doctor’s prescription and are often more potent.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Painkillers
OTC painkillers are commonly used to manage mild to moderate spinal stenosis pain. These medications include:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol): Acetaminophen is an effective pain reliever that can help reduce pain and inflammation. It’s available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and dissolvable tablets.
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin): Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that can help reduce pain, inflammation, and fever. It’s available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and gels.
- Aspirin: Aspirin is a pain reliever that can help reduce pain and inflammation. It’s often used to treat mild to moderate spinal stenosis pain.
Prescription Painkillers
Prescription painkillers are often used to manage severe spinal stenosis pain that doesn’t respond to OTC medications. These medications include:
- Narcotics (oxycodone, hydrocodone): Narcotics are strong painkillers that can help manage severe pain. However, they can be addictive and should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Muscle relaxants (cyclobenzaprine, carisoprodol): Muscle relaxants can help relieve muscle stiffness and spasms associated with spinal stenosis pain.
- Topical painkillers (lidocaine, capsaicin): Topical painkillers can be applied directly to the skin over the painful area to help reduce pain and inflammation.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While painkillers can be effective in managing spinal stenosis pain, they can also have potential risks and side effects. It’s essential to use painkillers under the guidance of a healthcare professional and follow the recommended dosage and usage guidelines. Common potential risks and side effects of painkiller use include:
- Digestive problems (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach ulcers)
- Allergic reactions (hives, itching, difficulty breathing)
- Drowsiness and dizziness
- Addiction and dependence
- Interactions with other medications
Medical Treatment and Alternatives

For individuals suffering from spinal stenosis, finding effective relief from pain and discomfort is a top priority. Medical treatment, along with alternative therapies and lifestyle changes, can significantly alleviate the symptoms associated with this condition.
Role of Physical Therapy in Relieving Spinal Stenosis Pain
Physical therapy plays a vital role in managing spinal stenosis pain. A physical therapist can develop a customized exercise program to strengthen the back and abdominal muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance posture. This can help reduce strain on the spinal cord, alleviate pressure, and promote more efficient movement.
- Stretching exercises can help maintain or improve range of motion and reduce stiffness in the spine.
- Strengthening exercises can enhance core stability, which supports the spine and promotes more efficient movement.
- Postural correction exercises can help re-educate the body to maintain proper alignment and reduce pressure on the spinal cord.
- Therapeutic modalities such as heat, cold, or electrical stimulation can be used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture and Chiropractic Care
Alternative therapies like acupuncture and chiropractic care have been used to manage spinal stenosis pain. While the underlying mechanisms are not yet fully understood, research suggests that these therapies can be beneficial in reducing pain and improving function.
- Acupuncture involves the insertion of fine needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the release of pain-relieving chemicals.
- Chiropractic care focuses on spinal manipulation and adjustment to improve mobility, reduce pressure, and alleviate pain.
- Some studies suggest that acupuncture and chiropractic care can be effective in reducing spinal stenosis pain, particularly when combined with other forms of treatment.
Lifestyle Changes to Alleviate Spinal Stenosis Pain
Lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in alleviating spinal stenosis pain. By making informed choices about diet, exercise, and sleep, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall quality of life.
- A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce inflammation.
- Regular exercise, such as walking or yoga, can improve flexibility, strengthen the back and abdominal muscles, and promote better posture.
- Getting adequate rest and avoiding prolonged sitting or heavy lifting can help reduce strain on the spinal cord.
Common Painkillers for Spinal Stenosis
When it comes to managing spinal stenosis pain, painkillers can be an essential part of a treatment plan. However, it’s crucial to choose the right painkiller to avoid side effects and ensure effective pain relief.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
Acetaminophen, commonly known by the brand name Tylenol, is often recommended as a first-line treatment for spinal stenosis pain. It works by blocking the production of prostaglandins, which are hormone-like substances in the body that can cause pain and inflammation. Acetaminophen is available over-the-counter (OTC) and is generally well-tolerated, but it’s essential to follow the recommended dosage to avoid liver damage. A study published in the Journal of Pain Research found that acetaminophen was effective in reducing pain in patients with spinal stenosis, with 70% of participants experiencing significant pain relief.
- Recommended dosage: 500-1000mg every 4-6 hours as needed
- Maximum daily dose: 4000mg
- Contraindicated in patients with liver disease or alcohol abuse
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a class of painkillers that can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Common NSAIDs for spinal stenosis pain include ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve). These medications work by blocking the production of prostaglandins and can be effective in reducing pain and inflammation. However, NSAIDs can have side effects such as stomach upset, nausea, and diarrhea. A study published in the Journal of Rheumatology found that NSAIDs were effective in reducing pain and improving function in patients with spinal stenosis, but were associated with a higher risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin): 200-400mg every 4-6 hours as needed
- Naproxen (Aleve): 250-500mg every 6-8 hours as needed
- Contraindicated in patients with stomach ulcers or bleeding disorders
Muscle Relaxants
Muscle relaxants, such as cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril), can help relieve muscle spasms and provide pain relief. These medications work by blocking nerve impulses that can cause muscle spasms. A study published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management found that cyclobenzaprine was effective in reducing muscle spasms and improving pain relief in patients with spinal stenosis. However, muscle relaxants can have side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and nausea.
- Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril): 5-10mg every 4-6 hours as needed
- Maximum daily dose: 80mg
- Contraindicated in patients with heart disease or arrhythmias
Natural Pain Relief Options

For individuals with spinal stenosis, finding alternative methods to manage pain is crucial, especially when medications or invasive procedures are not suitable. Natural pain relief options offer a holistic approach to alleviate discomfort and improve overall well-being. This section explores the use of herbal supplements, omega-3 fatty acids, and heat and cold therapy for pain relief.
Herbal Supplements: Turmeric and Ginger, What is the best painkiller for spinal stenosis
Turmeric and ginger are two popular herbal supplements that have been extensively studied for their potential pain-relieving properties. Turmeric contains a compound called curcumin, which has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Ginger, on the other hand, has been shown to reduce pain and inflammation by blocking the production of prostaglandins, which are hormone-like substances responsible for pain and inflammation. Both herbs can be consumed in the form of capsules, tea, or added to meals as a spice.
- Turmeric: Turmeric has been shown to reduce pain and inflammation in individuals with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. A study published in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine found that curcumin supplementation reduced pain and improved function in individuals with knee osteoarthritis.
- Ginger: Ginger has been used for centuries to reduce nausea and pain. A study published in the European Journal of Pain found that ginger extract reduced pain and inflammation in individuals with osteoarthritis of the knee.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fatty acids that have potent anti-inflammatory effects. They can be found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts. Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, have been shown to reduce pain and inflammation in individuals with spinal stenosis. A study published in the Journal of Pain Research found that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation reduced pain and improved function in individuals with spinal stenosis.
- EPA and DHA: These two omega-3 fatty acids have potent anti-inflammatory effects and have been shown to reduce pain and inflammation in individuals with spinal stenosis.
- Fatty fish: Fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids and have been shown to reduce pain and inflammation in individuals with spinal stenosis.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapy are two simple and effective methods to manage pain and discomfort associated with spinal stenosis. Heat therapy involves applying warmth to the affected area to increase blood flow and relax muscles. Cold therapy, on the other hand, involves applying ice or cold packs to the affected area to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Heat therapy: Heat therapy can be applied using a warm bath, shower, or heating pad. Heat therapy has been shown to reduce pain and improve function in individuals with spinal stenosis.
- Cold therapy: Cold therapy can be applied using an ice pack or cold compress. Cold therapy has been shown to reduce pain and inflammation in individuals with spinal stenosis.
Over-the-Counter Medications
When managing the pain associated with spinal stenosis, over-the-counter (OTC) medications can be a convenient and cost-effective option. However, it’s essential to understand the effectiveness and potential side effects of these medications to make an informed decision.
OTC painkillers are widely available and can be purchased without a prescription. The primary types of OTC painkillers used to manage spinal stenosis pain include acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and aspirin. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each medication is crucial in finding the most suitable option for individual needs.
Types of OTC Painkillers
The primary types of OTC painkillers used to manage spinal stenosis pain include:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol): Acetaminophen is an effective pain reliever that can be used to manage mild to moderate pain associated with spinal stenosis. However, it’s essential to follow the recommended dosage to avoid liver damage.
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin): Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. It’s often used in combination with other medications to manage spinal stenosis pain.
- Aspirin: Aspirin is a common OTC pain reliever that can be used to manage mild to moderate pain. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking aspirin, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions or take other medications.
Topical Pain Relievers
Topical pain relievers are creams, ointments, or patches applied directly to the skin over the painful area. These medications can provide localized pain relief without the systemic side effects associated with oral medications.
- Capsaicin cream: Capsaicin is a natural pain reliever that can be found in chili peppers. Capsaicin cream is applied topically to the painful area and can provide relief by blocking the production of a chemical called substance P, which transmits pain signals to the brain.
- Menthol and methyl salicylate: These topical pain relievers work by cooling the skin and reducing inflammation. They can be found in products such as heat wrap or cold pack.
OTC Medication Combinations
In some cases, combining OTC painkillers may be necessary to manage spinal stenosis pain. However, it’s essential to follow the recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare professional before taking any combinations of medications.
| Combination | Description |
|---|---|
| Acetaminophen and ibuprofen | Combining acetaminophen and ibuprofen can provide effective pain relief for mild to moderate pain associated with spinal stenosis. However, follow the recommended dosages to avoid liver damage and bleeding risks. |
| Ibuprofen and aspirin | Combining ibuprofen and aspirin can provide effective pain relief for moderate to severe pain associated with spinal stenosis. However, follow the recommended dosages to avoid bleeding risks. |
Prescription Pain Relievers: What Is The Best Painkiller For Spinal Stenosis
For individuals experiencing intense pain due to spinal stenosis, prescription painkillers can offer significant relief. These medications are carefully prescribed by healthcare providers to manage severe pain that may not respond to over-the-counter options or alternative pain relief methods.
Oxycodone (OxyContin) and Hydromorphone (Dilaudid)
Oxycodone and hydromorphone are two prescription opioid painkillers commonly used in the management of chronic pain associated with spinal stenosis. Both medications work by interacting with opioid receptors in the brain to produce feelings of pain relief and relaxation. However, it’s essential to use these medications as directed by a healthcare professional, as they can be habit-forming and potentially lead to addiction.
When taken according to the prescribed regimen, oxycodone (OxyContin) and hydromorphone (Dilaudid) can provide effective pain relief. However, it’s crucial to discuss the potential risks and benefits with a doctor before starting these medications. A thorough evaluation will help identify the most suitable treatment plan for each individual, considering factors like medical history, medication sensitivities, and lifestyle.
Fentanyl
Fentanyl, a potent synthetic opioid, is another prescription painkiller used for severe pain management in patients with spinal stenosis. When administered via transdermal patches or injectable forms, fentanyl can offer rapid pain relief and extended release. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions provided by a healthcare professional to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Fentanyl can be an effective pain management option for individuals with severe pain due to spinal stenosis. However, due to its high potency, it’s vital to monitor vital signs closely and adjust the dosage accordingly. As with other prescription painkillers, fentanyl should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as excessive use can lead to serious complications, including respiratory depression or overdose.
Injectable Painkillers: Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a type of injectable painkiller used to treat inflammation and swelling associated with spinal stenosis. These medications are administered directly into the spinal canal to reduce pressure on the spinal cord and surrounding nerves. Corticosteroids can provide temporary pain relief and can help reduce inflammation, allowing patients to regain mobility and function.
When administered by a qualified healthcare professional in a sterile environment, corticosteroid injections can be a valuable treatment option for patients suffering from spinal stenosis. However, it’s crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the risks, including side effects like increased blood sugar levels and changes in blood pressure.
In some cases, corticosteroid injections may not provide long-term relief, and subsequent injections may be necessary to maintain the pain-relieving effects. It’s essential to discuss treatment options with a healthcare provider, who can help determine the best course of action for each individual’s unique condition.
Lifestyle Changes for Pain Relief
Making significant lifestyle adjustments can have a substantial impact on pain relief for individuals suffering from spinal stenosis. While medical treatment and pain management options are crucial, incorporating healthy habits into daily life can bring long-term benefits and improve overall well-being.
Regular Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise and physical activity are essential for maintaining a healthy back and managing spinal stenosis symptoms. Engaging in moderate-intensity exercises, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, can help improve flexibility, strengthen back muscles, and reduce pain. It is recommended to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program, especially if the individual has any underlying medical conditions or concerns.
- Start with low-intensity exercises, gradually increasing the intensity and duration as the body adapts.
- Pelvic tilts, knee to chest stretches, and cat-cow stretches can be beneficial for spinal flexibility and mobility.
- Core-strengthening exercises, such as bridges and planks, can help stabilize the spine and reduce pain.
- Engage in regular activities, like gardening, yoga, or tai chi, to improve flexibility and balance.
Regular exercise can also have a positive impact on mental health, reducing stress and anxiety levels, which are often related to spinal stenosis symptoms.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is critical for individuals with spinal stenosis. Excess weight can put additional pressure on the spine, exacerbating symptoms and making it more challenging to manage pain. Aiming for a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce pressure on the spine and alleviate symptoms.
Aiming for a body mass index (BMI) between 18.5 and 24.9 can help reduce the risk of spinal stenosis symptoms and complications.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress management techniques are essential for individuals with spinal stenosis, as stress can exacerbate symptoms and make it more challenging to manage pain. Practicing stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, can help alleviate stress and anxiety levels.
“Stress can trigger muscle tension, which can worsen spinal stenosis symptoms. Finding healthy outlets for stress, such as meditation or yoga, can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.”
Examples of stress management techniques include:
- Meditation: Practice mindfulness meditation, transcendental meditation, or loving-kindness meditation to reduce stress and anxiety levels.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Practice slow, deliberate breathing to calm the mind and body.
- Yoga: Engage in gentle yoga exercises or practice relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation, to reduce stress and anxiety levels.
- Mindfulness Activities: Engage in activities that promote mindfulness, such as tai chi, walking, or journaling.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes into daily life, individuals with spinal stenosis can improve their overall well-being, manage symptoms, and reduce the risk of complications.
Last Recap
In conclusion, the best painkiller for spinal stenosis depends on individual factors, such as the severity of the condition, personal medical history, and treatment preferences. A multidisciplinary approach that incorporates a combination of painkillers, alternative therapies, and lifestyle changes can help manage spinal stenosis pain effectively.
Expert Answers
What are the common symptoms of spinal stenosis?
Symptoms of spinal stenosis may include pain, numbness, and weakness in the legs and back, as well as difficulty walking and balance problems.
Can spinal stenosis be cured?
Spinal stenosis is a chronic condition that cannot be cured, but it can be managed effectively with treatment and lifestyle changes.
What are the risks of using painkillers for spinal stenosis?
The risks of using painkillers for spinal stenosis include addiction, side effects, and interactions with other medications.
Are there any alternative therapies for spinal stenosis pain?
Yes, alternative therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, and physical therapy can help manage spinal stenosis pain.