Delving into the best part of meat, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, highlighting the crucial role of quality meat in enhancing culinary experiences. Understanding the factors that determine the quality of meat, such as breed, feed, and handling, is essential for selecting the perfect cuts for various cooking methods.
The best part of meat is often debated, with enthusiasts arguing over the merits of different cuts, cooking techniques, and pairing options. By exploring the diverse world of meat, including its types, nutritional content, and cultural significance, readers can become more informed and adept in their meat-based culinary endeavors.
Meat Quality
Meat quality is a critical aspect that affects the overall dining experience. The tenderness, flavor, and texture of meat are largely influenced by various factors, making it essential to understand what contributes to high-quality meat.
Determinants of Meat Quality
The quality of meat is determined by several factors, including breed, feed, and handling. These variables play a significant role in shaping the final product, impacting both its nutritional value and consumer satisfaction.
Breeds, for instance, are categorized into different groups based on their growth rate, feed efficiency, and carcass characteristics. Some popular breeds known for their meat quality include Angus, Wagyu, and Hereford. Their unique characteristics, such as marbling (the intramuscular fat that contributes to tenderness and flavor) and muscle fiber composition, contribute to the overall quality of the meat.
Feed, on the other hand, affects the nutritional profile and flavor of the meat. Grass-fed livestock, for example, tend to produce leaner and more nutritious meat, whereas grain-fed animals may have a higher fat content but a more intense flavor.
Handling is another critical factor that influences meat quality. The way livestock are handled from birth to slaughter can impact their stress levels, which directly affects their meat quality. Proper handling techniques, such as minimal stress and humane slaughter, can result in higher-quality meat with better flavor and texture.
Tenderness, Flavor, and Texture
Meat tenderness, flavor, and texture are closely linked to the factors mentioned above. Breed, feed, and handling all contribute to the final product, allowing consumers to experience a range of sensations when consuming meat.
- Tenderness is influenced by the muscle fiber composition and marbling of the meat. Grass-fed beef, for example, tends to be leaner and thus more tender.
- Flavor is affected by the feed and breed of the livestock. Grain-fed animals, for instance, may have a more intense flavor due to the high-energy diet.
- Texture is shaped by the way the meat is handled, particularly during slaughter and processing. Proper handling techniques minimize muscle degradation and result in a more uniform texture.
High-quality meat is characterized by its tenderness, flavor, and texture. Consumers can look for signs like marbling, a good balance of fat and lean meat, and a proper aging process to ensure the best possible taste and texture.
Examples of high-quality meats include dry-aged beef, which has undergone a specific aging process to enhance its flavor and tenderness; and grass-fed lamb, known for its lean and nutritious profile.
Types of Meat
When it comes to meat, there’s a staggering array of options to choose from. Each type of meat has its own unique characteristics, nutritional profile, and flavor profile. Understanding the different types of meat can help you make informed choices about what you put on your plate.
Meat diversity is one of the things that makes the world of food so fascinating. From the grasslands of Argentina to the oceans of Japan, different regions have their own specialty meats that are shaped by local tastes, traditions, and climates. Here are some of the most popular types of meat, categorized by their origins and characteristics.
Red Meats
Red meats come from mammals and are known for their rich flavor and tender texture. They tend to be higher in fat and cholesterol than white meats, but are often rich in essential nutrients like iron and zinc.
- Beef: Cattle are raised globally for their high-quality meat, with popular breeds like Angus and Wagyu prized for their marbling and tenderness.
- Pork: Pigs are one of the most widely consumed mammals in the world, with their meat used in a variety of dishes from charcuterie to barbecued ribs.
- Lamb: A popular choice in Mediterranean cuisine, lamb is known for its strong flavor and tender texture.
White Meats
White meats come from birds and fish, and are often lower in fat and calories than red meats. They’re also rich in protein and omega-3 fatty acids, which make them a popular choice for health-conscious eaters.
- Poultry: Chicken and turkey are two of the most widely consumed birds in the world, with their meat used in a variety of dishes from fried chicken to roasted turkey.
- Fish and Seafood: Fish and seafood come in a staggering array of species, with popular choices like salmon, tuna, and shrimp prized for their flavor and nutritional profile.
Game Meats
Game meats come from wild animals, and are often prized for their unique flavor and texture. They can be challenging to find and cook, but are a great choice for adventurous eaters.
- Venison: Deer meat is a popular choice in hunting cultures, with its lean flavor and tender texture making it a favorite among chefs.
- Wild Boar: A type of game meat that’s prized for its strong flavor and lean texture.
Nutritional Comparison Table
The nutritional content of different meats varies significantly, with some options being higher in fat and calories than others. Here’s a comparison table of some popular meats:
| Meat | Protein (% of daily value) | Fat (% of daily value) | Cholesterol (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beef (lean) | 22g (44% DV) | 4g (6% DV) | 60mg |
| Pork (lean) | 23g (46% DV) | 2g (3% DV) | 70mg |
| Lamb | 20g (40% DV) | 6g (9% DV) | 60mg |
| Chicken (breast) | 25g (50% DV) | 3g (5% DV) | 60mg |
| 20g (40% DV) | 10g (15% DV) | 60mg |
Best Cuts of Meat

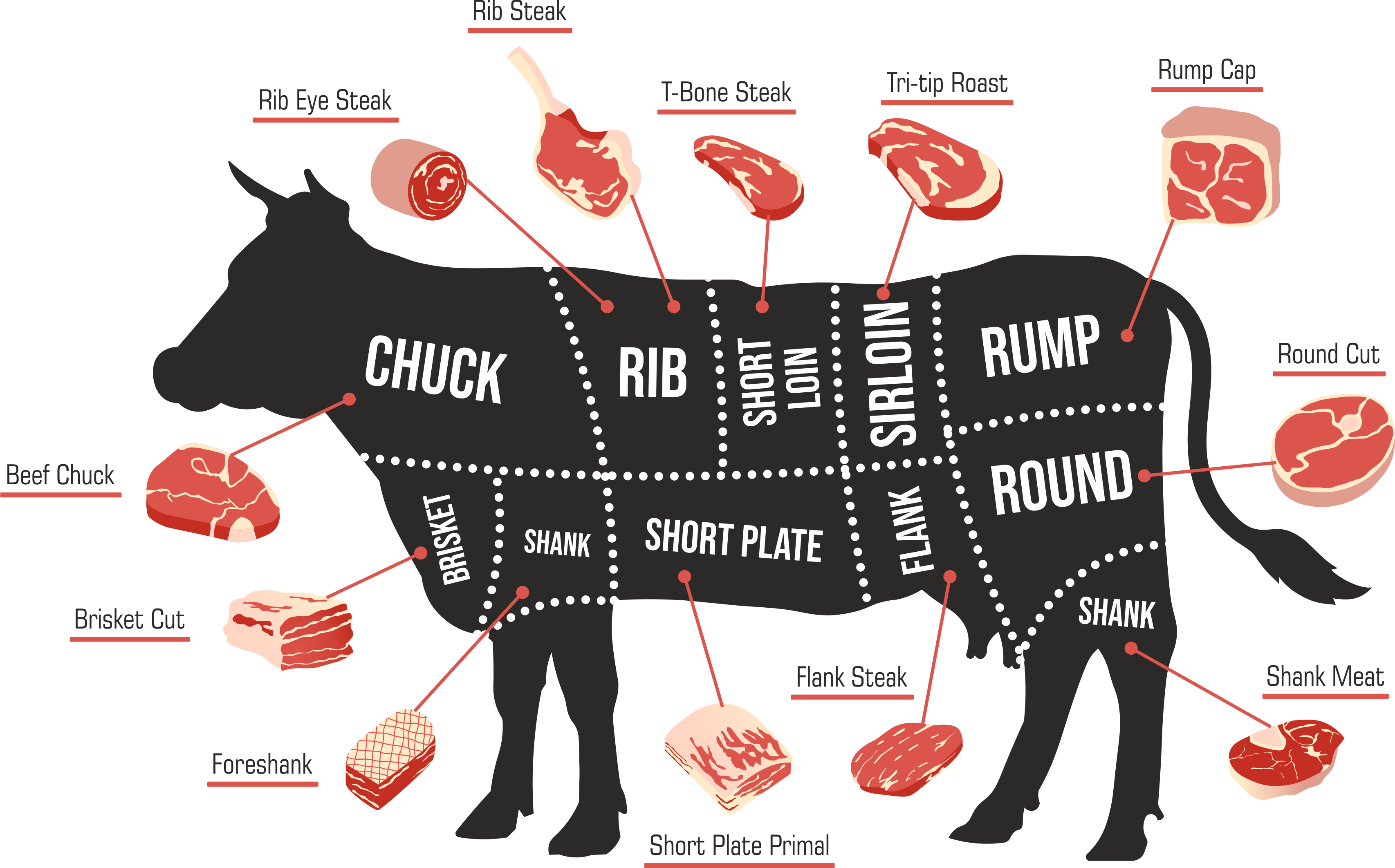
When it comes to the world of meat, the cut of the meat is just as important as the type of meat itself. The cut of the meat refers to the specific part of the animal from which the meat is obtained, and it can greatly affect the tenderness, flavor, and overall quality of the meat. In this section, we will explore the different cuts of meat, how they are obtained, and which cuts are best suited for various cooking methods.
Different Cuts of Meat
Meat cuts are obtained from different parts of the animal, including the primal cuts, sub-primals, and retail cuts. The primal cuts are the initial cuts made on the animal, which are then further divided into sub-primals and retail cuts. Here are some of the main types of primal cuts:
- Boston butt (upper portion of the front leg)
- Chuck (shoulder and neck area)
- Rib (ribcage area)
- Round (hindquarters)
- Short loin (lower back area)
- Tenderloin (shortest part of the spine)
These primal cuts are then further divided into sub-primals, which are cuts that are still large and rough but can be trimmed and cut into retail cuts. Retail cuts are the final cuts of meat that are sold in stores and are typically ready to cook. The most common retail cuts include:
- Steaks (e.g. ribeye, sirloin, filet mignon)
- Roasts (e.g. prime rib, beef round)
- Ground meat (e.g. ground beef, ground pork)
Best Cuts for Different Cooking Methods
Different cooking methods require different cuts of meat, depending on the level of tenderness and flavor desired. Here are some of the best cuts for various cooking methods:
- Grilling: Ribeye, Sirloin, T-bone
- Roasting: Prime rib, Beef round, Leg of lamb
- Slow cooking: Chuck, Short ribs, Lamb shanks
These cuts are ideal for specific cooking methods because they have the right level of tenderness and marbling (the streaks of fat that are dispersed throughout the meat). Grilling requires cuts that are tender and have a good balance of fat and lean meat, while roasting requires cuts that are larger and have a high level of marbling. Slow cooking requires cuts that are tougher and have more connective tissue, which breaks down and becomes tender with slow cooking.
Factors that Affect the Quality and Tenderness of Cuts
The quality and tenderness of a cut of meat are affected by several factors, including the animal’s diet, living conditions, age, and breed. The following are some of the key factors that affect the quality and tenderness of a cut of meat:
- Marbling: Marbling is the streaks of fat that are dispersed throughout the meat. Meats with more marbling are typically more tender and flavorful.
- Age: Younger animals typically produce more tender meat, while older animals produce meat that is tougher and more flavorful.
- Breed: Different breeds of animals are bred for specific characteristics, such as size, meat quality, and production efficiency. Some breeds, such as Grass-fed beef, are known for producing higher-quality meat.
- Fat content: Meats with a higher fat content are typically more tender and flavorful, while meats with a lower fat content are leaner and less tender.
The factors that affect the quality and tenderness of a cut of meat are complex and multifaceted. However, by understanding these factors and selecting the right cut for the cooking method and desired outcome, cooks can ensure that they are getting the best possible meat for their recipes.
The Role of Genetics in Meat Quality
Genetics play a significant role in determining the quality and tenderness of a cut of meat. Different breeds of animals are bred for specific characteristics, such as size, meat quality, and production efficiency. Some breeds, such as Grass-fed beef, are known for producing higher-quality meat.
For example, Grass-fed beef is typically more tender and flavorful than grain-fed beef due to the higher levels of marbling and more favorable fatty acid profile.
Meat quality is also influenced by the animal’s genetics, with some breeds being naturally more inclined to produce high-quality meat. For example, Angus cattle are known for producing some of the most tender and flavorful beef in the world due to their genetic makeup.
The Role of Nutrition in Meat Quality
Nutrition also plays a significant role in determining the quality and tenderness of a cut of meat.
For example, animals that are fed a diet rich in nutrients and omega-3 fatty acids tend to produce higher-quality meat with better marbling and flavor.
A diet rich in nutrients and healthy fats helps to promote the development of tenderness and flavor in meat. Conversely, a diet that is deficient in essential nutrients and healthy fats can lead to meat that is tough and lacking in flavor.
Preserving Meat Quality
Meat quality can also be affected by the way it is preserved and stored.
For example, meat that is stored at the correct temperature and humidity level will stay fresh for longer and retain its quality.
Proper handling and storage of meat are essential for preserving its quality and preventing spoilage. Meat should be stored at a temperature of around 40°F (4°C) and should be kept away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of meat is complex and multifaceted, with numerous factors affecting the quality and tenderness of a cut of meat. By understanding these factors and selecting the right cut for the cooking method and desired outcome, cooks can ensure that they are getting the best possible meat for their recipes. Additionally, genetics, nutrition, and preservation play important roles in determining meat quality, and proper handling and storage of meat can help to preserve its quality and prevent spoilage.
Meat Pairing and Recipes

Meat pairing and recipes is an art that requires balance, contrast, and a deep understanding of flavors and textures. It’s about creating harmonious combinations that elevate the natural flavors of the meat, while also considering the preferences, dietary needs, and cultural influences of the diners. Whether you’re cooking for a special occasion or simply want to spice up your everyday meals, mastering the art of meat pairing and recipes can take your cooking to the next level.
The Art of Meat Pairing
Meat pairing is about matching the bold, rich flavors of the meat with complementary flavors and textures that enhance its natural flavor profile. This can be achieved by considering the characteristics of the meat, such as its tenderness, fattiness, and seasonings, and pairing it with ingredients that balance, contrast, or amplify these qualities. For example, a robust, high-fat cut of meat like short ribs can be paired with a tangy, acidic sauce like BBQ or a zesty, herby marinade to cut through its richness.
When pairing meats, consider the following key principles:
– Balance: Balance the strong flavors of the meat with lighter, brighter flavors like citrus, herbs, or spices.
– Contrast: Contrast the texture and flavor of the meat with crunchy, crisp textures like fresh vegetables or crunchy nuts.
– Complement: Complement the flavor of the meat with ingredients that share similar flavor profiles, such as beef with mushrooms or pork with apples.
Recipe Ideas for Different Types of Meat, Best part of meat
Here are some delicious recipe ideas that showcase the versatility of meat pairing and recipes:
– Beef Wellington: Tender filet mignon wrapped in puff pastry with mushrooms, herbs, and gravy.
– Korean BBQ Beef Tacos: Marinated beef short ribs grilled and served in tacos with spicy Korean chili flakes, kimchi slaw, and cilantro.
– Beef and Guinness Stew: Hearty, comforting stew made with slow-cooked beef, Guinness stout, and root vegetables.
– Pork Carnitas Tacos: Slow-cooked pork shoulder, shredded and fried until crispy, served in tacos with pickled onions, cilantro, and salsa.
– Grilled Pork Chops with Apple Cider Jus: Thick-cut pork chops grilled and served with a sweet, tangy apple cider jus and roasted vegetables.
– Pork and Vegetable Dumplings: Steamed dumplings filled with a mixture of ground pork, shredded cabbage, and ginger, served with a side of soy sauce and chili oil.
– Lemon and Herb Roasted Lamb Chops: Tender lamb chops roasted with a bright, citrusy lemon and herb marinade and served with roasted vegetables.
– Lamb Koftas with Tzatziki Sauce: Skewers of lamb meat, grilled and served with a refreshing tzatziki sauce made with yogurt, cucumber, and garlic.
– Beef and Lamb Meatball Subs: Hearty meatballs made with ground beef and lamb, topped with marinara sauce and melted mozzarella cheese.
Important Tips for Meat Pairing
–
Always season your meat liberally with salt, pepper, and any other desired spices before cooking to ensure a balanced flavor.
–
Use a variety of ingredients to add texture, flavor, and visual appeal to your dishes.
–
Don’t be afraid to experiment and try new combinations of flavors and ingredients to find your own unique voice in the kitchen.
Meat and Nutrition
Meat is an essential component of a balanced diet, providing essential nutrients that support overall health and well-being. It is a rich source of protein, vitamins, and minerals, making it a vital part of a healthy eating plan.
Meat can be an excellent source of various essential nutrients, including iron, zinc, and B vitamins. However, the nutritional benefits of meat can vary depending on the type and cut, as well as cooking methods. Lean cuts of meat, such as sirloin and chicken breast, are lower in saturated fat and higher in nutrients than processed meats like sausages and bacon.
Nutritional Benefits of Meat
Meat is a rich source of protein, which is essential for building and repairing tissues in the body. It also contains various vitamins and minerals, including:
- Iron: An essential mineral that plays a crucial role in red blood cell production and oxygen transport. Adequate iron intake is essential to prevent anemia.
- Zinc: A mineral that supports immune function, wound healing, and protein synthesis. Zinc deficiency can lead to impaired growth and development.
- B vitamins: A group of vitamins that play a crucial role in energy metabolism, nerve function, and heart health. Meat is a rich source of thiamin, riboflavin, and niacin.
Nutritional Drawbacks of Meat
While meat can be a nutritious part of a balanced diet, it can also have negative effects on health if consumed excessively. Some of the potential drawbacks of meat consumption include:
- High saturated fat content: Processed meats like sausages and bacon contain high amounts of saturated fat, which can contribute to heart disease and other cardiovascular problems.
- Foodborne illnesses: Meat can be contaminated with bacteria like E. coli and Salmonella, which can cause foodborne illnesses.
- Antibiotic resistance: The overuse of antibiotics in livestock farming has contributed to the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, making infections more difficult to treat.
Healthy Meat-Based Recipes and Meal Ideas
Here are some healthy meat-based recipes and meal ideas that showcase the nutritional benefits of meat:
- Grilled chicken breast with roasted vegetables: A lean cut of chicken breast paired with a variety of roasted vegetables makes for a nutritious and flavorful meal.
- Salmon with quinoa and steamed broccoli: A rich source of omega-3 fatty acids and protein, salmon is paired with quinoa and steamed broccoli for a well-rounded meal.
- Braised beef short ribs with root vegetables: A lean cut of beef short ribs is slow-cooked in a flavorful broth with a variety of root vegetables for a comforting and nutritious meal.
Conclusive Thoughts: Best Part Of Meat
In conclusion, the best part of meat is a multifaceted topic that encompasses quality, variety, and cultural relevance. By embracing the nuances of meat, readers can elevate their cooking skills, experiment with new recipes, and appreciate the rich history and symbolism surrounding this essential food group.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the most tender type of meat?
Wagyu beef is often considered one of the most tender types of meat, with its unique marbling and rich flavor.
How can I safely thaw frozen meat?
It’s essential to thaw frozen meat in a covered container, allowing it to thaw in the refrigerator or under cold running water.
What are some tips for grilling the best cuts of meat?
For a perfect grilled cut, ensure the meat reaches an internal temperature of 135°F (57°C) for medium-rare, and brush with oil or marinade before cooking.
Can I cook meat from frozen without thawing it first?
Yes, but ensure you follow proper cooking times and internal temperatures to prevent foodborne illness.
How can I prevent cross-contamination when handling raw meat?
Always handle raw meat separately from cooked foods, wash your hands thoroughly, and use utensils and cutting boards for raw meat only.